本文最后更新于 2024年8月6日 下午
hot100题解 哈希 两数之和 1. 两数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) {int [] res = new int [2 ];new HashMap <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {int temp = target - nums[i];if (map.containsKey(temp)) {0 ] = i;1 ] = map.get(temp);break ;return res;
字母异味词分组 49. 字母异位词分组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams (String[] strs) {new HashMap <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < strs.length; ++i) {char [] chars = strs[i].toCharArray();String temp = String.valueOf(chars);new ArrayList <String>());return new ArrayList <List<String>>(map.values());
最长连续序列 128. 最长连续序列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 0 )return 0 ;int count = 1 ;int res = count;for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ])continue ;if (nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] + 1 )else {1 ;return res = Math.max(res, count);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) {new HashSet <Integer>();for (int num : nums) {int longestStreak = 0 ;for (int num : num_set) {if (!num_set.contains(num - 1 )) {int currentNum = num;int currentStreak = 1 ;while (num_set.contains(currentNum + 1 )) {1 ;1 ;return longestStreak;
双指针 移动零 283. 移动零 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) {int count = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {if (nums[i] != 0 )for (int i = count; i < nums.length; ++i)0 ;
盛水最多的容器 11. 盛最多水的容器 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public int maxArea (int [] height) {int i = 0 , j = height.length - 1 ;int max = 0 ;while (i < j) {int l = j - i;int h = height[i] < height[j] ? height[i] : height[j];if (height[i] <= height[j])else return max;
三树之和 15. 三数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) {new ArrayList <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {if (nums[i] > 0 )return res;if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ])continue ;int left = i + 1 ;int right = nums.length - 1 ;while (right > left) {int sum = nums[left] + nums[i] + nums[right];if (sum > 0 )else if (sum < 0 )else {while (right > left && nums[left] == nums[left + 1 ]) left++;while (right > left && nums[right] == nums[right - 1 ]) right--;return res;
接雨水 42. 接雨水 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public int trap (int [] height) {int [] maxLeft = new int [height.length];int [] maxRight = new int [height.length];0 ] = height[0 ];for (int i = 1 ; i < height.length; ++i)1 ]);1 ] = height[height.length - 1 ];for (int i = height.length - 2 ; i >= 0 ; --i)1 ]);int sum = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < height.length - 1 ; ++i) {int v = Math.min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]) - height[i];if (v > 0 )return sum;
滑动窗口 无重复字符的最长字串 3. 无重复字符的最长子串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) {int len = s.length();if (len == 0 )return 0 ;new HashSet <>();int right = -1 , res = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < len; ++i) {if (i != 0 )1 ));while (right + 1 < len && !set.contains(s.charAt(right + 1 ))) {1 ));1 );return res;
找到字符串中所有字母异位词 438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public List<Integer> findAnagrams (String s, String p) {new ArrayList <>();int [] cnt = new int [26 ];for (int i = 0 ; i < p.length(); ++i)'a' ]++;int l = 0 ;for (int r = 0 ; r < s.length(); ++r) {'a' ]--;while (cnt[s.charAt(r) - 'a' ] < 0 ) {'a' ]++;if (r - l + 1 == p.length())return res;
子串 和位K的子数组 560. 和为 K 的子数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) {new HashMap <>();0 , 1 );int sum = 0 , count = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {0 );0 ) + 1 );return count;
覆盖滑动窗口的最大值 239. 滑动窗口最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) {int n = nums.length;int [] res = new int [n - k + 1 ];new ArrayDeque <>();for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) {while (!q.isEmpty() && nums[q.getLast()] <= nums[i])if (i - q.getFirst() >= k)if (i >= k - 1 )1 ] = nums[q.getFirst()];return res;
最小覆盖字串 76. 最小覆盖子串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public String minWindow (String s, String t) {char [] S = s.toCharArray();int m = S.length;int ansLeft = -1 ;int ansRight = m;int left = 0 ;int [] cntS = new int [128 ];int [] cntT = new int [128 ];for (char c : t.toCharArray())for (int right = 0 ; right < m; ++right) {while (isCovered(cntS, cntT)) {if (right - left < ansRight - ansLeft) {return ansLeft < 0 ? "" : s.substring(ansLeft, ansRight + 1 );public boolean isCovered (int [] cntS, int [] cntT) {for (int i = 'A' ; i <= 'Z' ; ++i)if (cntS[i] < cntT[i])return false ;for (int i = 'a' ; i <= 'z' ; ++i)if (cntS[i] < cntT[i])return false ;return true ;
数组 最大子数组和 53. 最大子数组和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路
遍历此数组,用于一个变量记录累加值,在累加过程中,只要不小于0,那么就更新最大值,如果小于0,直接令为0,遍历完成后,即可得到最大值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) {int res = 0 ;int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {if (res < 0 )0 ;return max;
合并区间 56. 合并区间 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路
先将数组按照左端点大小排序,创建一个列表,然后进行对数组进行遍历,如果当前列表的长度大于0并且最后一个元素的左端点值小于等于当前遍历元素的右端点值 ,就更新列表中元素的右端点值为最大值,如果不满足以条件 ,就把当前元素加入到列表中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution {public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) {int []> res = new LinkedList <>();return a[0 ] - b[0 ];for (int [] p : intervals) {int m = res.size();if (m > 0 && p[0 ] <= res.get(m - 1 )[1 ])1 )[1 ] = Math.max(res.get(m - 1 )[1 ], p[1 ]);else return res.toArray(new int [res.size()][]);
轮转数组 189. 轮转数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路
先将轮转数k对数组长度取余,然后先反转整个数组,再反转元素0至k-1,最后再反转元素k至末尾元素即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public void rotate (int [] nums, int k) {int size = nums.length;if (k > 0 ) {0 , size - 1 );0 , k - 1 );1 );public void change (int [] nums, int left, int right) {while (left < right) {int tmp = nums[left];
除自身以外数组的乘积 238. 除自身以外数组的乘积 - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路
先用两个数组分别存储数组的前缀乘积和后缀乘积,然后把对应的前缀乘积和后缀乘积相乘即可得到
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int [] productExceptSelf(int [] nums) {int size = nums.length;int [] pre = new int [size];int [] post = new int [size];0 ] = 1 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < size; ++i)1 ] * nums[i - 1 ];1 ] = 1 ;for (int i = size - 2 ; i >= 0 ; --i)1 ] * nums[i + 1 ];int [] answer = new int [size];for (int i = 0 ; i < size; ++i)return answer;
缺失的第一个正数(待优化) 41. 缺失的第一个正数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:hard
解题思路
设置res为1,先将数组排序,然后遍历数组,如果元素比res大,直接返回,如果比res小,跳过,否则res增加。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution {public int firstMissingPositive (int [] nums) {int res = 1 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; ++i) {if (nums[i] > 0 ) {if (res < nums[i])return res;else if (res > nums[i])continue ;else return res;
矩阵 矩阵置零 73. 矩阵置零 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
记录首行和首列置零信息,然后将非首行和非首列为0的元素映射到首行和首列,然后根据首行和首列信息进行各行各列置零,最后再根据记录的信息判断是否进行首行首列元素置零。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution {public void setZeroes (int [][] matrix) {int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0 ].length;boolean r0 = false , c0 = false ;for (int i = 0 ; i < m; ++i) {if (matrix[i][0 ] == 0 ) {true ;break ;for (int j = 0 ; j < n; ++j) {if (matrix[0 ][j] == 0 ) {true ;break ;for (int i = 1 ; i < m; ++i) {for (int j = 1 ; j < n; ++j)if (matrix[i][j] == 0 )0 ] = matrix[0 ][j] = 0 ;for (int j = 1 ; j < n; ++j) {if (matrix[0 ][j] == 0 ) {for (int i = 1 ; i < m; ++i)0 ;for (int i = 1 ; i < m; ++i) {if (matrix[i][0 ] == 0 )0 );if (r0) {for (int i = 0 ; i < m; ++i)0 ] = 0 ;if (c0)0 ], 0 );
螺旋矩阵 54. 螺旋矩阵 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) {new ArrayList <>();int left = 0 , right = matrix[0 ].length - 1 , top = 0 , bottom = matrix.length - 1 ;while (left <= right || bottom >= top) {for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i)if (bottom < ++top)break ;for (int i = top; i <= bottom; ++i)if (left > --right)break ;for (int i = right; i >= left; --i)if (--bottom < top)break ;for (int i = bottom; i >= top; --i)if (++left > right)break ;return list;
旋转图像 48. 旋转图像 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
先将整个矩阵转置,再将矩阵最左列和最右列元素互换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public void rotate (int [][] matrix) {int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0 ].length;for (int i = 0 ; i < m; ++i) {for (int j = 0 ; j < i; ++j) {int tmp = matrix[i][j];int left = 0 , right = n - 1 ;while (left < right) {for (int i = 0 ; i < m; ++i) {int tmp = matrix[i][left];
搜索二维矩阵 240. 搜索二维矩阵 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
从右上角开始找,如果相等直接返回,如果大于target,舍弃这一列,小于target,舍弃这一行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution {public boolean searchMatrix (int [][] matrix, int target) {int i = 0 , j = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ;while (i < matrix.length && j >= 0 ) {if (matrix[i][j] == target)return true ;if (matrix[i][j] < target)else return false ;
链表 相交链表 160. 相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {if (headA == null || headB == null )return null ;ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;while (pA != pB) {null ? headB : pA.next;null ? headA : pB.next;return pA;
反转链表 206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
新建一个头结点,然后遍历链表中的节点,用头插法依次插入到头结点后即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) {if (head == null )return null ;ListNode newHead = new ListNode (-1 );null ;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null ) {ListNode temp = cur.next;return newHead.next;
回文链表 234. 回文链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
先利用快慢指针找到链表的中间节点,然后,将链表的后半部分反转,两个链表依次比较得到结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution {public boolean isPalindrome (ListNode head) {ListNode mid = returnMid(head);ListNode head2 = reverse(mid);while (head != null && head2 != null ) {if (head.val != head2.val)return false ;return true ;public ListNode returnMid (ListNode head) {ListNode slow = head, fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) {return slow;public ListNode reverse (ListNode head) {ListNode prev = null ;ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null ) {return prev;
环形链表 141. 环形链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
快慢指针,慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,如果相遇,则相交,否则不相交
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class Solution {public boolean hasCycle (ListNode head) {if (head == null )return false ; ListNode slow = head;ListNode fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) {if (slow == fast)return true ;return false ;
环形链表Ⅱ 142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
题解 :142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) {ListNode slow = head, fast = head;while (fast != null && fast.next != null ) {if (slow == fast) {while (slow != head) {return slow;return null ;
合并两个有序链表 21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
比较两个链表元素的大小,逐个尾插较小的节点即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {if (list1 == null && list2 == null )return null ;ListNode newHead = new ListNode (-1 );ListNode r = newHead;ListNode p1 = list1;ListNode p2 = list2;while (p1 != null && p2 != null ) {if (p1.val < p2.val) {else {null ;if (p1 != null )if (p2 != null )return newHead.next;
两数相加 2. 两数相加 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
记录两个链表上元素的值,记录余数,记录进位值,然后进行计算即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {public ListNode addTwoNumbers (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode head = new ListNode (-1 );ListNode cur = head;int x = 0 , y = 0 , k = 0 , now = 0 ;while (l1 != null || l2 != null || k != 0 ) {null ? 0 : l1.val;null ? 0 : l2.val;10 ;10 ;ListNode node = new ListNode (now);if (l1 != null )if (l2 != null )null ;return head.next;
删除链表的倒数第N个结点 19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
快慢指针,快指针先走n步,接着和满指针同步走,当快指针走完时,慢指针就指向了被删除结点的前面一个结点,然后删除即可,记住要加头结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) {ListNode newHead = new ListNode (-1 );ListNode fast = newHead, slow = newHead;for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; ++i)while (fast != null ) {return newHead.next;
两两交换链表中的节点 24. 两两交换链表中的节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 , head);ListNode node0 = dummy;ListNode node1 = head;while (node1 != null && node1.next != null ) {ListNode node2 = node1.next;ListNode node3 = node2.next;return dummy.next;
K个一组翻转链表 25. K 个一组翻转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:hard
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public ListNode reverseKGroup (ListNode head, int k) {int n = 0 ;for (ListNode cur = head; cur != null ; cur = cur.next) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 , head), preHead = dummy;ListNode pre = null , cur = head;for (; n >= k; n -= k) {for (int i = 0 ; i < k; ++i) {ListNode next = cur.next;ListNode tail = preHead.next;return dummy.next;
随机链表的复制 138. 随机链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:hard
解题思路
先再每一个节点后添加一个新节点,然后将新节点的random指针进行设置,最后拆分链表即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution {public Node copyRandomList (Node head) {if (head == null )return null ;Node p = head;while (p != null ) {Node newNode = new Node (p.val);while (p != null ) {if (p.random != null ) {Node dummy = new Node (-1 );Node cur = dummy;while (p != null ) {return dummy.next;
排序链表 148. 排序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
先用列表存储链表元素值,然后对列表排序,最后再逐一赋值给链表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) {if (head == null )return null ;new ArrayList <>();ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null ) {int i = 0 ;while (cur != null ) {return head;
合并K个升序链表 23. 合并 K 个升序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:hard
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution {public ListNode mergeKLists (ListNode[] lists) {new PriorityQueue <>((a, b) -> a.val - b.val);for (ListNode head : lists)if (head != null )ListNode dummy = new ListNode (); ListNode cur = dummy;while (!pq.isEmpty()) { ListNode node = pq.poll(); if (node.next != null ) return dummy.next;
LRU缓存 146. LRU 缓存 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 class LRUCache {private static class Node {int key, value;int k, int v) {private final int capacity;private final Node dummy = new Node (0 , 0 );private final Map<Integer, Node> keyToNode = new HashMap <>();public LRUCache (int capacity) {this .capacity = capacity;public int get (int key) {Node node = getNode(key);return node != null ? node.value : -1 ;public void put (int key, int value) {Node node = getNode(key);if (node != null ) {return ;new Node (key, value);if (keyToNode.size() > capacity) {Node backNode = dummy.prev;private Node getNode (int key) {if (!keyToNode.containsKey(key))return null ;Node node = keyToNode.get(key);return node;private void remove (Node x) {private void pushFront (Node x) {
二叉树 二叉树的中序遍历 94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
递归法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void inorder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> rel) {if (root == null )return ;
非递归 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <Integer>();new Stack <>();if (root != null )while (!stack.empty()) {TreeNode node = stack.peek();if (node != null ) {if (node.right != null )null );if (node.left != null )else {return rel;
二叉树的最大深度 104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
递归 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution {public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {if (root == null ) return 0 ;int lDepth = maxDepth(root.left);int rDepth = maxDepth(root.right);return Math.max(lDepth, rDepth) + 1 ;
非递归 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution {public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {new LinkedList <>();int rel = 0 ;if (root != null )while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int len = queue.size();while (len > 0 ) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null )if (node.right != null )return rel;
翻转二叉树 226. 翻转二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
采用递归法,逐一交换当前节点的左右孩子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) {return root;public void invert (TreeNode node) {if (node == null )return ;TreeNode tmp = node.left;
对称二叉树 101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
检查当前两个节点是否相等,如果相等,递归比较第一个节点的左子树和第二个节点的右子树以及第一个节点的右子树和第二个节点的左子树,最后如果两个都相等,则对称
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution {public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) {return judge(root.left, root.right);public boolean judge (TreeNode leftNode, TreeNode rightNode) {if (leftNode == null && rightNode == null ) return true ;if (leftNode == null && rightNode != null ) return false ;if (leftNode != null && rightNode == null ) return false ;if (leftNode.val != rightNode.val) return false ;boolean left = judge(leftNode.left, rightNode.right);boolean right = judge(leftNode.right, rightNode.left);return left && right;
二叉树直径 543. 二叉树的直径 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
采用递归法,求每个节点的左右子树高度之和,然后用一个变量sum记录最大的左右子树高度之和,最后遍历完成即可得到答案
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {int sum = 0 ;public int diameterOfBinaryTree (TreeNode root) {return sum;public int height (TreeNode root) {if (root == null )return 0 ;int leftHeight = height(root.left);int rightHeight = height(root.right);return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 ;
二叉数的层序遍历 102. 二叉树的层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
用队列来存储各个节点,将各个节点的左右孩子依次入队,在遍历每层之前,先创建一个list,然后存储本层的节点,遍历完成再加入到大的list里面即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <List<Integer>>();new LinkedList <>();if (root != null )while (!queue.isEmpty()) {new ArrayList <>();int len = queue.size();while (len > 0 ) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null )if (node.right != null )return rel;
将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
每次创建节点都选择区间数组中间节点,然后递归左子树和右孩子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) {return construct(nums, 0 , nums.length - 1 );public TreeNode construct (int [] nums, int left, int right) {if (left > right)return null ;int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ;TreeNode node = new TreeNode (nums[mid]);1 );1 , right);return node;
验证二叉树搜索树 98. 验证二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
不断更新左右边界的值,然后跟当前的元素值进行比较,如果都满足则继续递归,否则为false
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) {long left = Long.MIN_VALUE, right = Long.MAX_VALUE;return search(root, left, right);public boolean search (TreeNode root, long left, long right) {if (root == null )return true ;long x = root.val;return left < x && x < right && search(root.left, left, x) && search(root.right, x, right);
二叉搜索树中第K小的元素 230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {int res = 0 , count;public int kthSmallest (TreeNode root, int k) {return res;public void search (TreeNode root) {if (root == null )return ;if (--count == 0 ) {return ;
二叉树的右视图 199. 二叉树的右视图 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
采用中序遍历的方式,记录当前层的最后一个节点即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution {public List<Integer> rightSideView (TreeNode root) {new ArrayList <>();new LinkedList <>();if (root != null )while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int len = queue.size();while (len > 0 ) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (len == 1 )if (node.left != null )if (node.right != null )return rel;
二叉树展开为链表 114. 二叉树展开为链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
114. 二叉树展开为链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public void flatten (TreeNode root) {while (root != null ) { if (root.left == null ) {else {TreeNode pre = root.left;while (pre.right != null ) {null ;
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
代码随想录 (programmercarl.com)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution {new HashMap <>();public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) {for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; ++i)return findNode(preorder, 0 , preorder.length, inorder, 0 , inorder.length);public TreeNode findNode (int [] preorder, int preBegin, int preEnd, int [] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) {if (preBegin >= preEnd || inBegin >= inEnd)return null ;int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preBegin]);TreeNode node = new TreeNode (inorder[rootIndex]);int len = rootIndex - inBegin;1 , preBegin + len + 1 , inorder, inBegin, rootIndex);1 , preEnd, inorder, rootIndex + 1 , inEnd);return node;
路径综合Ⅲ(待优化) 437. 路径总和 III - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution {long sum = 0 ;int count = 0 ;public int pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root != null )if (root != null && root.left != null )if (root != null && root.right != null )return count;public void search (TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null )return ;if (sum == targetSum)long pre = sum;0 ;
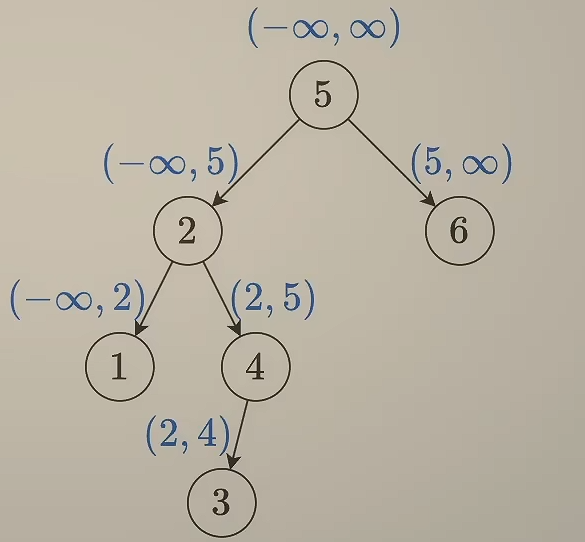
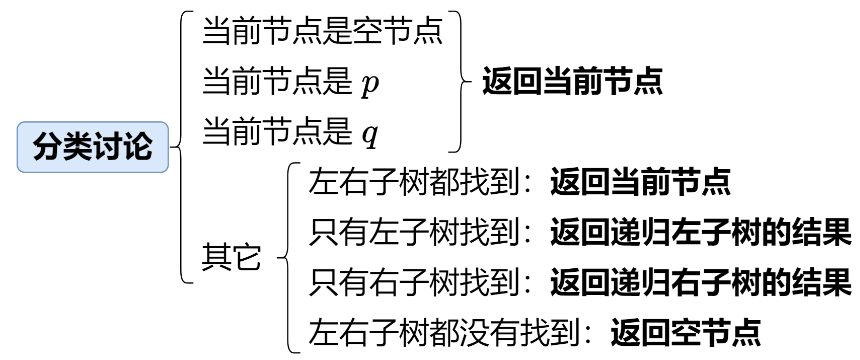
二叉树的最近公共祖先 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == p || root == q || root == null )return root;TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if (left == null && right == null )return null ;else if (left == null && right != null )return right;else if (left != null && right == null )return left;else return root;
二叉树中的最大路径和 124. 二叉树中的最大路径和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:hard
解题思路
找到每个子树的最大链和,然后递归左右子树,在递归过程中不断更新max的值来记录最大路径和
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {private int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public int maxPathSum (TreeNode root) {return ans;private int dfs (TreeNode node) {if (node == null ) {return 0 ; int lVal = dfs(node.left); int rVal = dfs(node.right); return Math.max(Math.max(lVal, rVal) + node.val, 0 );
贪心 买卖股票的最佳时机 121. 买卖股票的最佳时机 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:easy
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution {public int maxProfit (int [] prices) {int max = 0 ;int minPrice = prices[0 ];for (int p : prices) {return max;
跳跃游戏 55. 跳跃游戏 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
记录当前可到达范围内的最大下标,如果整个值大于或等于数组的最后一个下标,那么就可到达,否则不可到达
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution {public boolean canJump (int [] nums) {if (nums.length == 1 )return true ;int cover = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i <= cover; ++i) {if (cover >= nums.length - 1 )return true ;return false ;
跳跃游戏Ⅱ 45. 跳跃游戏 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public int jump (int [] nums) {int count = 0 ;int end = 0 ;int next = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i <= end && end < nums.length - 1 ; ++i) {if (i == end) {return count;
划分字母区间 763. 划分字母区间 - 力扣(LeetCode)
难度:medium
解题思路
用一个哈希数组记录每个字母的最右侧边界,然后遍历字符串,在区间范围内对右边界进行更新,划分完成当前区间后,继续往后划分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution {public List<Integer> partitionLabels (String s) {new ArrayList <>();int [] hash = new int [26 ];int left = 0 , right = 0 ;for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); ++i)'a' ] = i;for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); ++i) {'a' ]);if (i == right) {1 );1 ;return res;